
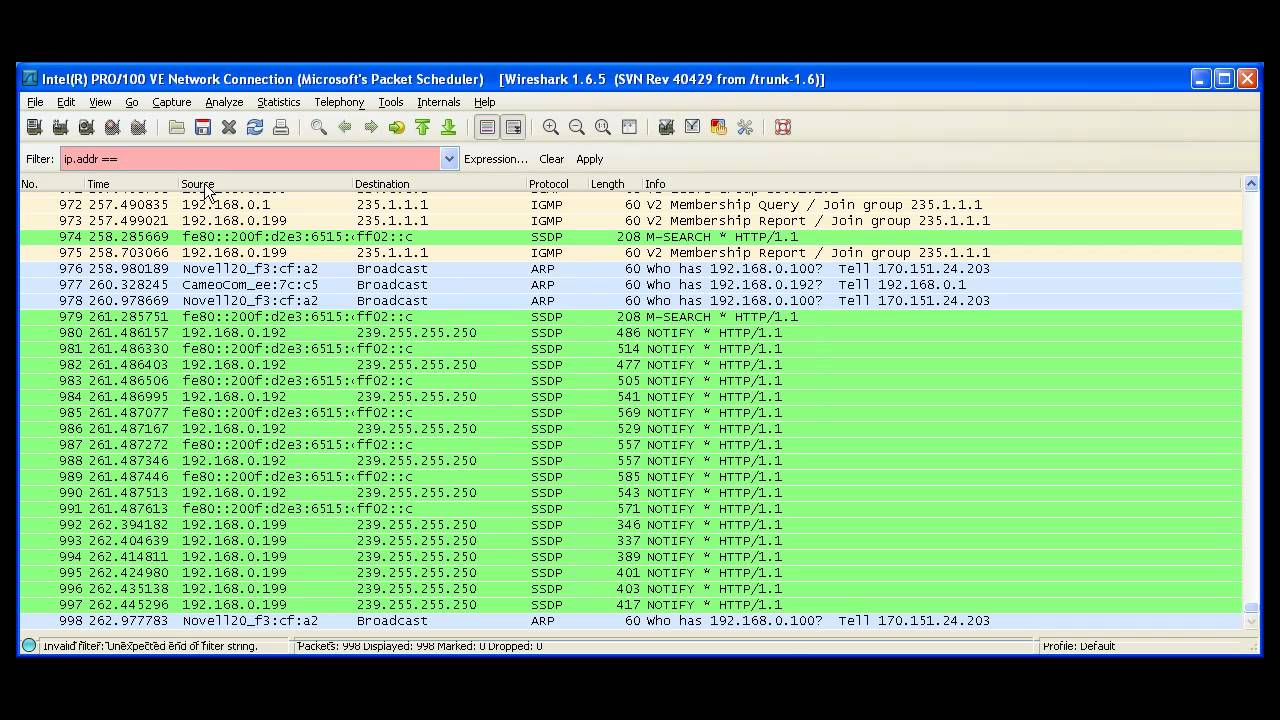
You're looking to obtain sensitive information such as credentials when a person logs in or registers at a website. You can also add your own colouring rules in case if you wanted all packets with incoming IP address matching x.x.x.x to be blue.Īttacking & Defending with Wireshark Attacking: This can be changed by going to View > Colouring Rules. Colour Coding PacketsĮach of the packets in the main view are colour-coded so we can easily understand what they mean. Wireshark offers a Flow Graph (under Statistics tab) where you're able to see how the communication works between a server and client. Sometimes it's difficult to grasp a picture of how the packets are flying. Here's a view of the in-depth and the bytes panel: Flow Graph For more details, go down to the In-depth panel and the bytes panel for more details on the packet flags, source and destination ports, HTTP form data, and more! This Info view is just meant to be a quick view of what the packet is about.Info – Provides additional details about the packet.Protocol means "a set of rules governing the format of data sent over the Internet or other network." Click here for a complete list.Protocol – Protocol name used in the packet.Destination – Destination address of the packet, could be an IP or MAC address.

As humans, we find it easier when the IP or MAC address is an actual name, such as 'or 'You can enable Wireshark's option to convert these addresses by going to "View > Name Resolution > Resolve Network Addresses".Source – Source address of the packet, could be an IP or MAC address.You can change this to various other time formats by going to "View > Time Display Format >.a.k.a how much time passed since you began capturing.Right below the toolbar, there are seven columns: Here's a look at what the buttons on the toolbar do. When you begin capturing network packets, the following window will show up. Sometimes, packets bounce of various hosts asking for a final destination - at this point, Wireshark keeps the packet or discards based on this option. Promiscious Mode enabled means if a packet is not meant for your system, Wireshark will still keep a record of it. Once selected, press Capture.Īfter you click capture, the following display shows up confirming your selection and offers a few more configurations. To capture more than one interface, simply hold the 'command' key (for Mac) and then select.'awdl0' is for my bluetooth chip and 'Loopback: lo0' is for my local server. A wired interface would be the built-in Thunderbolt ports I have.
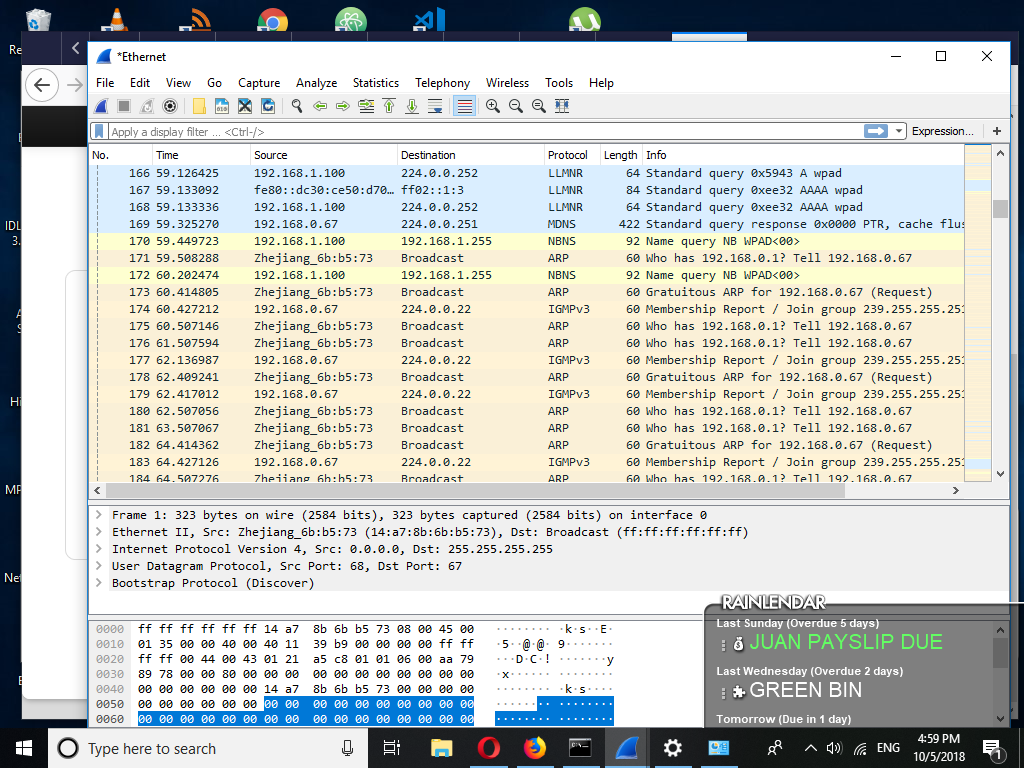
'All Interfaces shown' drop down menu allows you to select between Wired, Wireless and External interfaces.The 'Capture' button begins the network capture.Wireshark captures network information from the Application Layer to the Link Layer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
